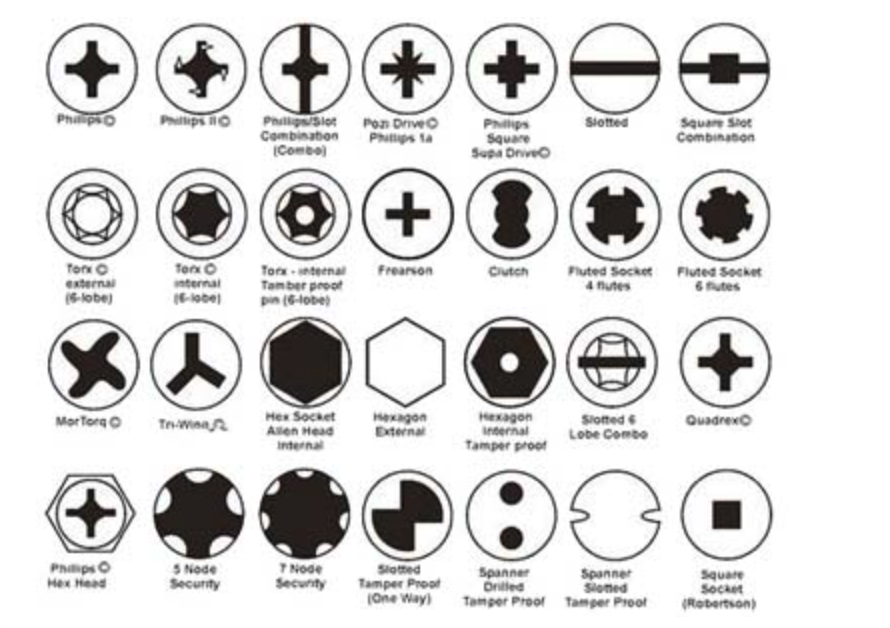
Introduction to Tweezers: History, Types, and Features
Tweezers are a simple yet ingenious tool that plays an indispensable role in our daily lives and professional work. From medical and beauty applications to the repair of precision electronic devices, tweezers have a wide range of uses. However, for most people, tweezers might only seem like an insignificant small tool. In this article, we will delve into the origins, development, classification, and features of tweezers to help buyers gain a better understanding of this essential instrument. The history of tweezers can be traced back to ancient times. The earliest tweezers may have appeared during the Bronze Age. Archaeologists have discovered early tweezer tools in ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman sites. They were usually made of metal or bone, simple in structure, yet highly functional for various tasks such as medical procedures, crafts, and everyday tasks. As time progressed, the design and materials of tweezers continued to improve. In medieval Europe, blacksmiths began crafting more refined iron tweezers for medical and anatomical studies. In the East, ancient Chinese physicians also used tweezers for delicate acupuncture and herbal treatments. Following the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century, with advancements in metalworking, the manufacturing techniques and materials for tweezers saw significant improvements. Especially with the widespread use of stainless steel, modern tweezers gained better durability and corrosion resistance. Today’s tweezers are not only more diverse in design but have also achieved substantial advancements in functionality. Modern tweezers can perform delicate operations under a microscope, handle hair-thin components, and even execute complex surgeries in sterile medical environments. These tools have become indispensable in many professional fields. Modern tweezers come in a variety of types and can be classified based on different criteria such as usage, materials, and functionality. • Electronic Tweezers: Mainly used for handling electronic components and small parts. Often made with anti-static materials to prevent damage to sensitive components due to static electricity. • Medical Tweezers: Used in surgeries and laboratory operations, requiring sterile and stable materials. Usually made from stainless steel or titanium alloy, offering high corrosion resistance and easy sterilization. • Beauty Tweezers: Used for eyebrow shaping, nail art, false eyelashes, etc. These tweezers are typically lightweight and ergonomically designed for comfortable use. • Craft Tweezers: Used for handling small parts in crafts such as jewelry making and model assembly. • Stainless Steel Tweezers: The most common type, with good corrosion resistance and wear resistance, suitable for most applications. • Titanium Alloy Tweezers: Lightweight, high hardness, and excellent corrosion resistance. Commonly used in medical and precision electronics fields. • Ceramic Tweezers: Highly resistant to heat and non-magnetic, suitable for handling sensitive electronic components or high-temperature environments. • Plastic Tweezers: Lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for simple operations that do not require high material standards, such as chemical handling in laboratories. • Precision Tweezers: Typically have very fine and precise tips, suitable for operations under a microscope and for handling micro-sized components. • Angled Tweezers: The tips are angled to provide a better view during operation, suitable for handling objects in confined spaces. • Straight Tweezers: The most common type, suitable for most gripping and holding tasks. • Anti-static Tweezers: Made from anti-static materials or coated with anti-static layers to prevent electrostatic discharge damage to electronic components, making them the tool of choice in the electronics industry. Different types of tweezers have their unique features and advantages during use: 1. Anti-static Properties: Anti-static tweezers are usually made from carbon fiber, plastic, or metal with an anti-static coating. These tweezers can effectively prevent static discharge from damaging sensitive electronic components and are widely used in electronics manufacturing and repair. 2. Corrosion Resistance: Tweezers made from stainless steel and titanium alloy have excellent corrosion resistance. Especially in medical and laboratory environments, where tweezers frequently come into contact with various chemical reagents and disinfectants, corrosion-resistant tweezers ensure long-term use. 3. Hardness and Toughness: Titanium alloy and ceramic tweezers have high hardness and are not easily deformed or worn out. Although ceramic tweezers are harder, they are also more brittle and are suitable for scenarios requiring high hardness but no metal use, such as the assembly of high-frequency circuits. 4. Non-magnetic Properties: Non-magnetic tweezers are crucial in scenarios where magnetic interference must be avoided, such as in the repair of precision instruments or handling minute metallic substances in laboratories. 5. Ergonomic Design: Tweezers used in beauty and medical scenarios often consider user comfort and operational stability. The length, curvature, and grip design of the handles are meticulously crafted for ergonomic use. As a simple yet sophisticated tool, tweezers come in many types and serve various purposes. From an ancient medical tool to an essential instrument in modern electronics manufacturing, tweezers play an irreplaceable role in different fields. By understanding their classifications and features, buyers can choose the most suitable tweezers for different applications. In the next article, we will delve into the manufacturing processes and quality control of tweezers, helping you understand the story behind high-quality tweezers.Historical Background
1. By Usage:
2. By Material:
3. By Function:
Main Features of Tweezers
Conclusion
If you are looking for a professional screwdriver manufacturerto customize your precision screwdriver set, feel free to contact us today! We provide high-quality, customizable toolsfor various repair needs.
BECOME A WHOLESALE PARTNER
Get 10% off on orders over 500 units. We offer exclusive B2B pricing, OEM packaging, mixed batch support, and fast global delivery. Partner with a trusted screwdriver manufacturer to boost your margins.